A Way Forward with National Elections and State-building in Somalia
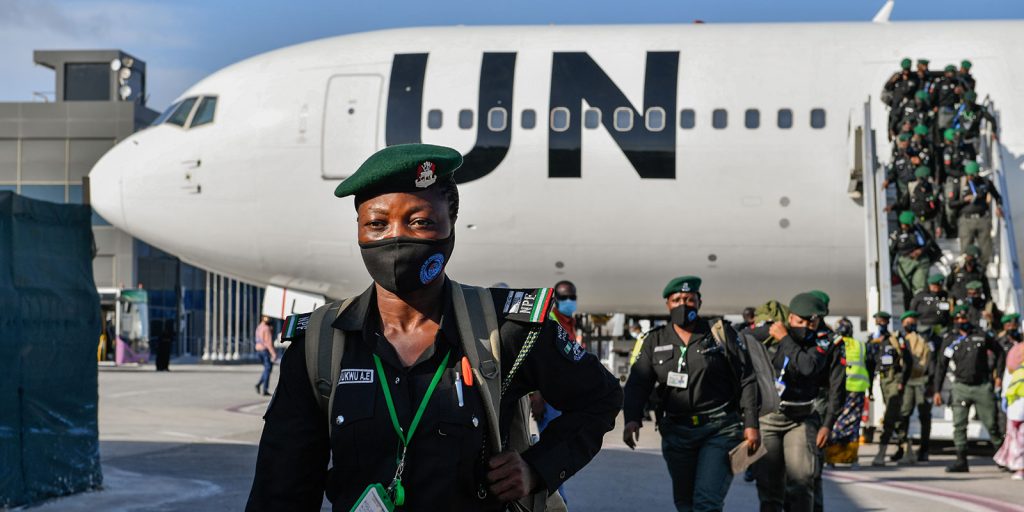

Following months of political impasse and rising tensions over the holding of elections in Somalia, the leaders of the Federal Government of Somalia and of the country’s Federal Member States signed a key agreement on 27 May that paves the way for elections. This was the culmination of several weeks of consensus-building efforts led by Prime Minister Mohamed Hussein Roble.
Somalia’s Arduous Election Journey
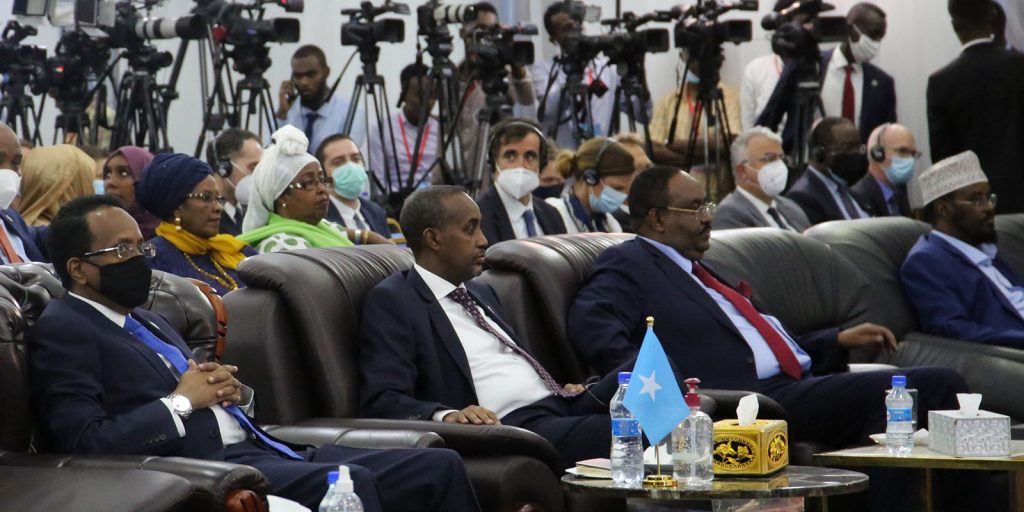

Since February, a series of rash political decisions took place that threw the country into chaos. Although the election deadlock has now been resolved and a new agreement reached on 27 May, the repercussions of the recent political drama are wide reaching.
How Somalia Averted a Civil War
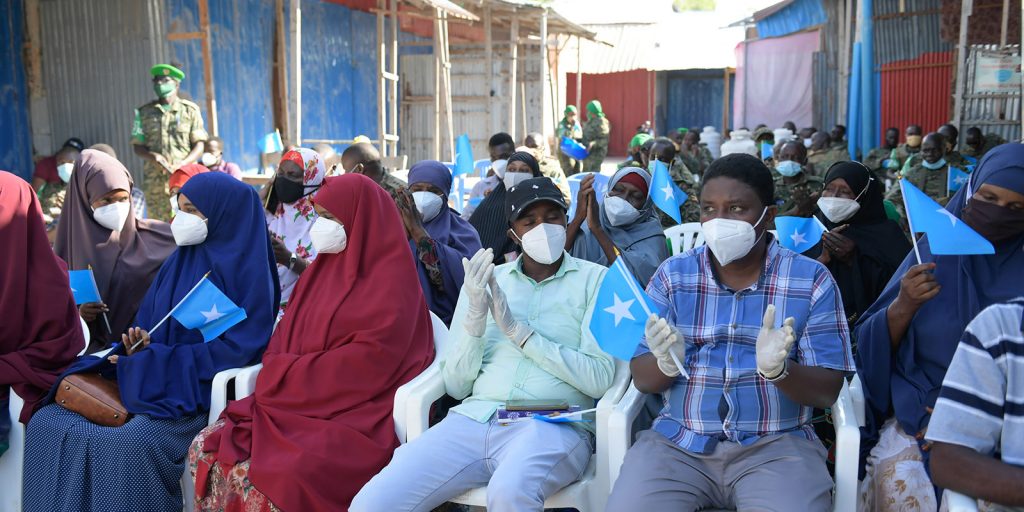

On 27 May 2021, the Federal Government of Somalia (FGS) and Federal Member States (FMS) signed a major agreement that would put the country back on an electoral pathway after months of intense political standoff over the type and process of elections. In late April, armed clashes broke out in the capital after the lower house of the bicameral parliament passed a controversial resolution extending its own mandate and that of President Mohamed Abdullahi Farmaajo by two years. The decision was rejected by almost all domestic political stakeholders in the country, as well as the overwhelming majority of the international community.
Strengthening Partnerships for African Solutions for African problems: Implications for peace support operations
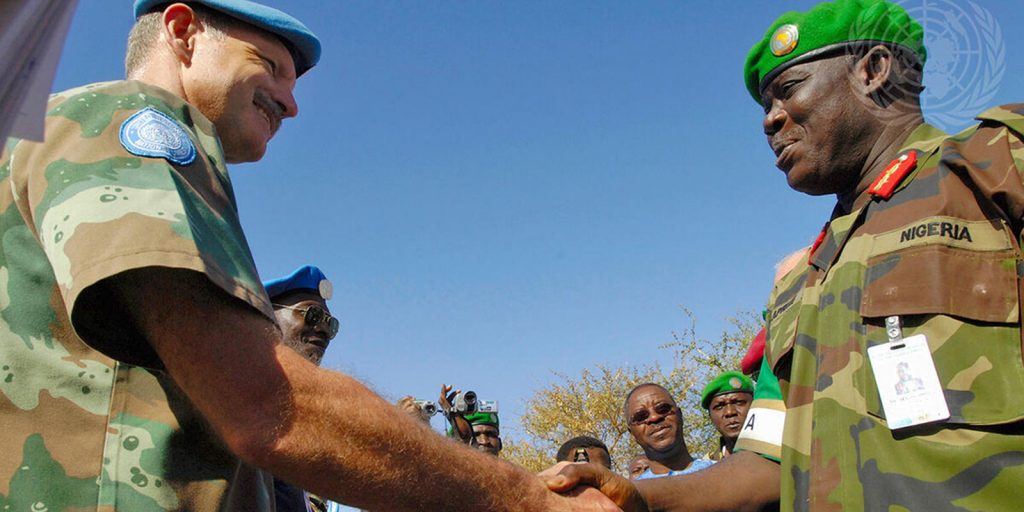

The expression “African Solutions for African problems” has become something of a cliché. It is frequently invoked when trying to develop effective solutions to address peace and security challenges on the continent. It is a phrase that has also been misused by some leaders to advance their interests while trying to avoid scrutiny of their actions in handling their own domestic peace and security challenges and invoking the phrase in an effort to engage the African Union (AU) to provide a face-saving mechanism which perhaps they hope to influence.
Inclusive conflict prevention is key to peace in Africa
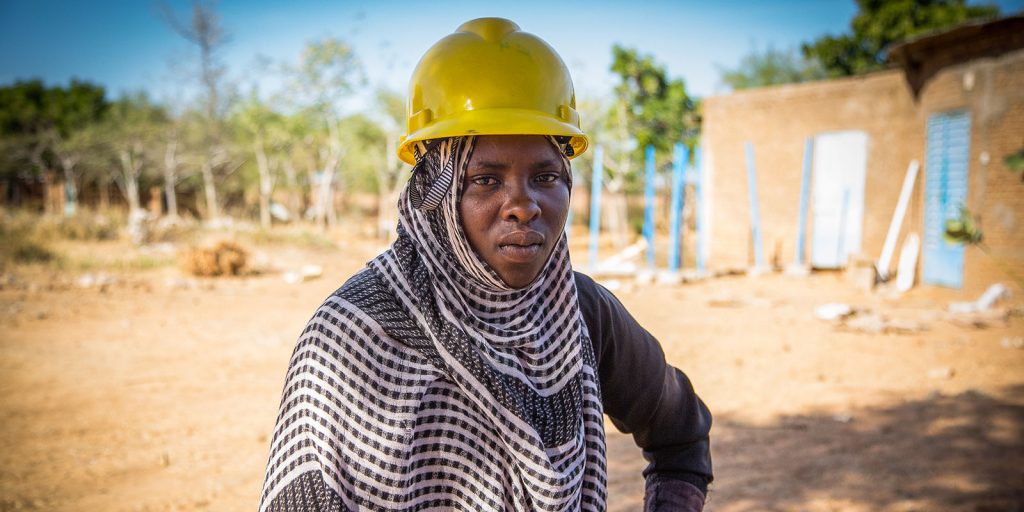

The key to a more stable and peaceful Africa lies in conflict prevention! Unfortunately, there is still reluctance, both by the international community and governments to invest in prevention. If we could focus more on prevention, much more could be achieved.
International support for the effectiveness of the G5 Sahel Force
At the UN Security Council and in other forums in Africa and Europe, diplomats are debating different options for increasing international support to the G5 Sahel Force. The aim is to enhance its operational capacity and effectiveness to restore stability in the Sahel. Despite the presence of the UN Stabilization Mission in Mali (MINUSMA), the Group of Five Sahel (G5 Sahel) Force, as well as French and European Union missions, the security situation in the Sahel has significantly deteriorated over the last few years.
Interrupting the Cycle of Violence in Cabo Delgado
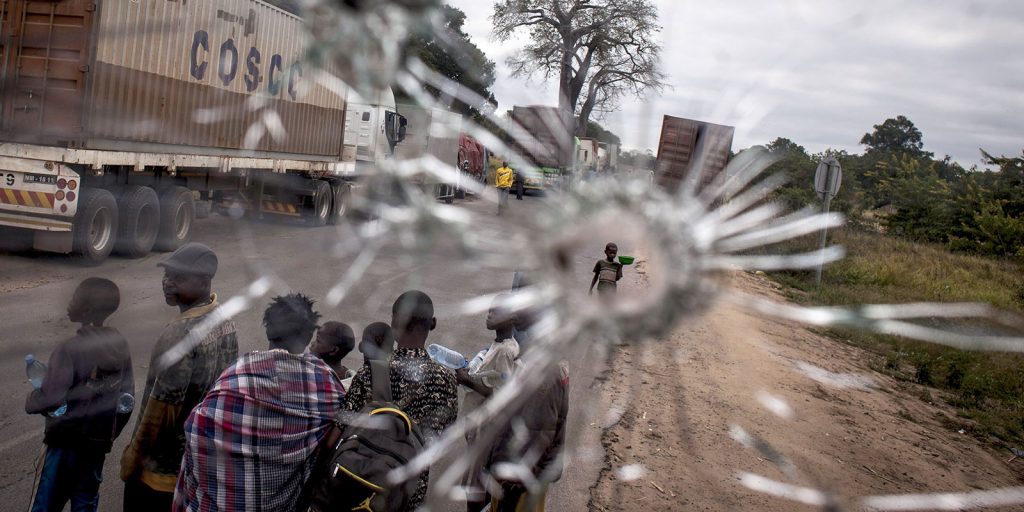

The conflict in the North of Cabo Delgado has been presented in international media as a phenomenon of terrorism and Islamic radicalization. This kind of analysis does not pay due attention to the political economy of the region, nor does it capture the complex internal and external causes of the phenomenon.
Promoting Peace in the Age of Compound Risk – Reflections and Lessons for Africa
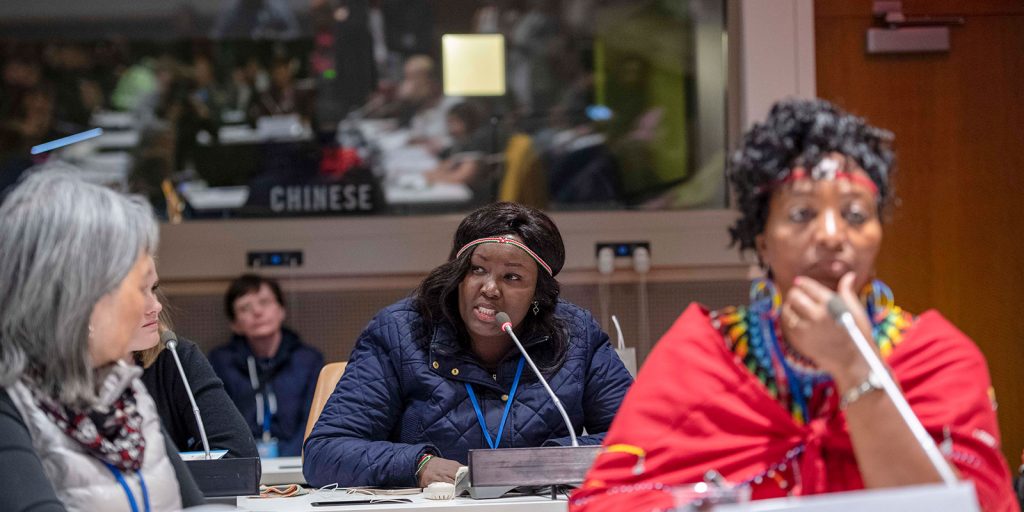

Indeed, in 2020, as we were planning to celebrate major instruments for the advancement of women’s rights to peace and development, namely the Beijing Declaration and Platform of Action and the United Nations Security Council Resolution 1325 (UNSCR 1325), the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic erupted, causing deaths and disruptions all over the world. The pandemic demonstrated once more that in times of crisis, women and girls bear the brunt of the impact and are the ones at the front of the risk.
Africa’s compound challenges need a collective response

We live in a peculiar moment in history in which prevailing threats to peace and stability have collided with a pandemic that occurs once in a century. For the African continent, it is rather a precarious moment in which our realities and limitations have come to the fore, more than in previous decades.
Shifting the Theory and Practice of Conflict Management to Respond to Current Conflict Contexts: A role for South Africa?

The changing conflict contexts have refocused our attention on the theory and practice of conflict management and the need for transforming the ways in which we seek to Silence the Guns in Africa. In the 1990s the conflict contexts demanded that peace be sought internally between identifiable warring parties with the ability to do harm, usually government and one or two rebel groups seeking access to political power; that mediation went beyond ceasefire agreements to deliver more comprehensive peace accords; and peacekeeping broadened to encompass multidimensional peace support operations.
