COVID-19 stresses Intra-SADC Trade

Intra-Southern African Development Community (SADC) exports and imports as a proportion of overall trade of the region rose from 15.2% and 17.5% to 19.5% and 19.15% respectively between 2008 and 2018. In their virtual meeting held in March 2020, the SADC Council of Ministers (SCM) observed that less than 20% of intra-SADC trade prevents member States from realising their economic potential. Thus, the above marginal intra-regional trade, firstly, reflects low industrialisation, evidenced by a slight increase in the manufacturing sector’s contribution to gross domestic product (GDP) from an average of 10.3% in 2013 to 11.9% in 2018. Secondly, this reflects lack of diversifying member States’ economic structures from agriculture and mining sectors, which in 2018, accounted for an average of over 25% of GDP. While in particular, South Africa, the largest and most diversified economy, has high capabilities of dominating intra-SADC trade.
The Impact of COVID-19: The Conundrum of South Africa’s Socio-Economic Landscape

Like all countries caught in the first wave of the COVID-19 Pandemic, the Ramaphosa government has had to take some tough decisions: ease into a hard lock-down regulation or take a softer but cautious approach. South Africa was quick out of the starting blocks opting for a hard lockdown that imposed strict curfew restrictions that only allowed certain essential sectors to operate, forced small and medium businesses to endure greater strain on their operations, limited social gatherings and urged social distancing and mask wearing as part of the personal protective measures. The harshest impact was on the alcohol and tobacco industries that saw the sale of these products being banned.
COVID-19’s second wave deepens Southern Africa’s rate of poverty and unemployment
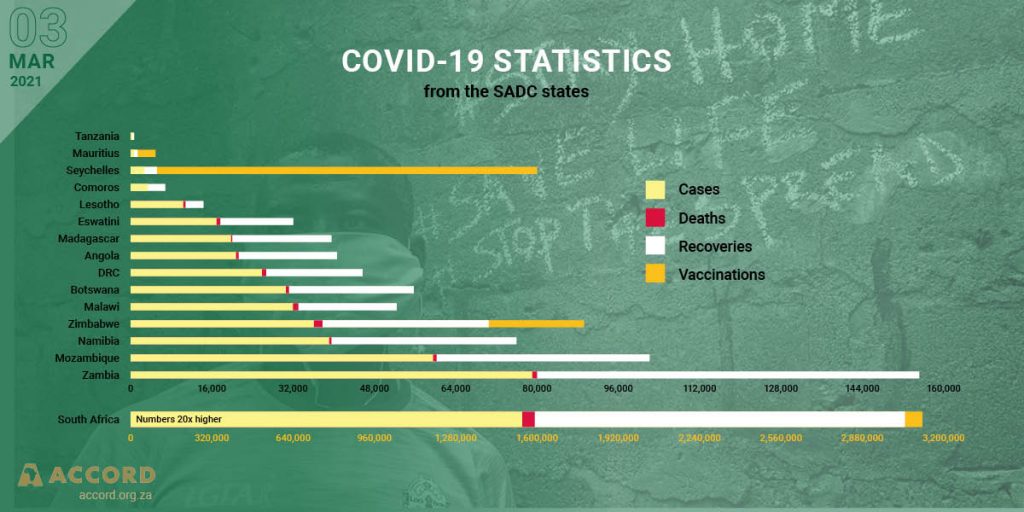
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed fragilities and fault lines in many African countries, particularly their health systems and economic vulnerabilities. In spite of varying degrees of development on the African continent, the impact of the virus has taken its toll on the social, economic and political fibres in most African societies. While the pandemic did not exacerbate security challenges as earlier anticipated initially; and the continent was able to manage its rate of infection at the onset of the pandemic; the second wave of the virus resulted in a reversion of some restrictions as previously enforced in the first wave of the virus, causing a threat to livelihoods, as well as a trust deficit between the state and citizens, particularly in South Africa and Zimbabwe.
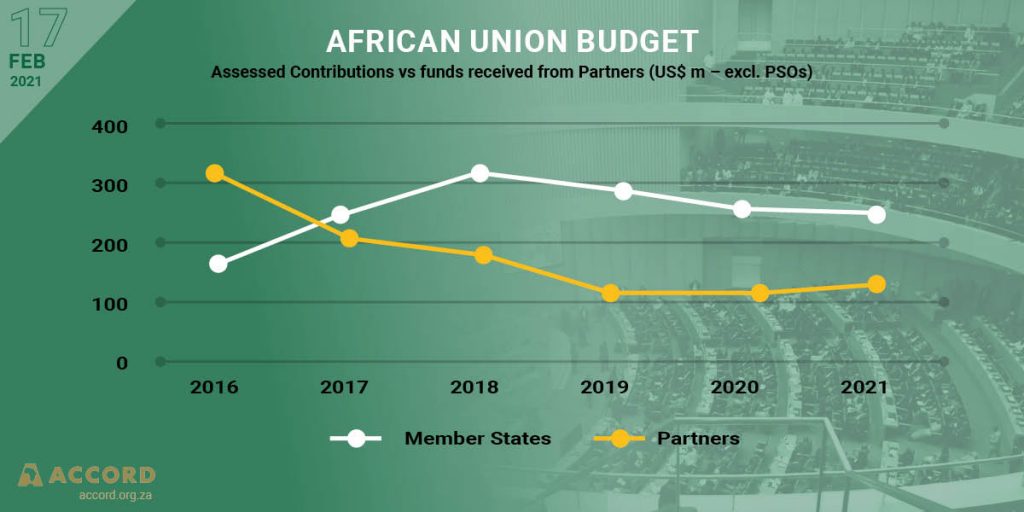
An African Union Summit held in the midst of COVID-19 pandemic and against growing tensions in parts of the continent
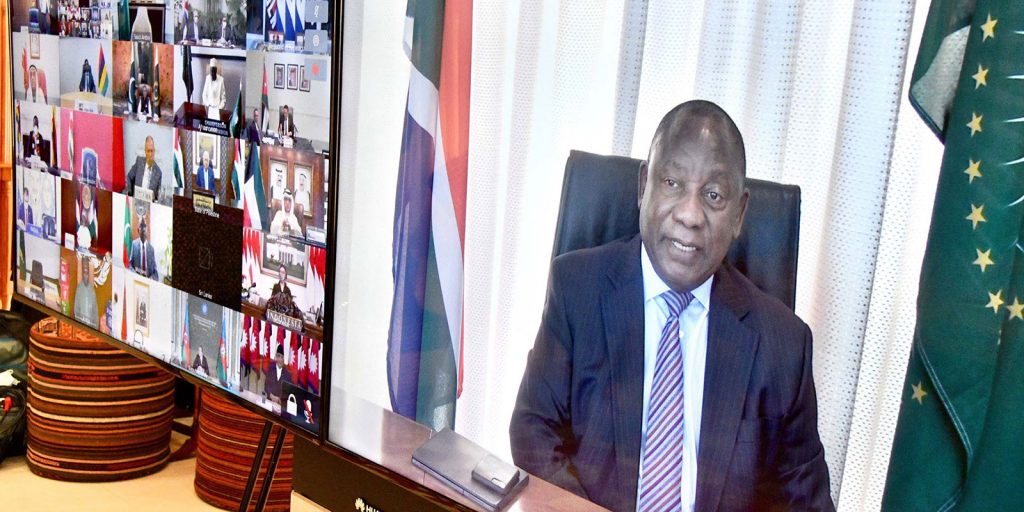

The 34th Ordinary Session of the African Union (AU) Assembly of Heads of State and Government was held virtually due to COVID-19 pandemic from the 6th-7th February 2021. The Summit focussed on Africa’s response to the COVID-19 Pandemic; progress in the AU institutional reform and the election of a new Bureau for the AU Commission.
Security in Somalia beyond 2021 – the future role of AMISOM and the international community
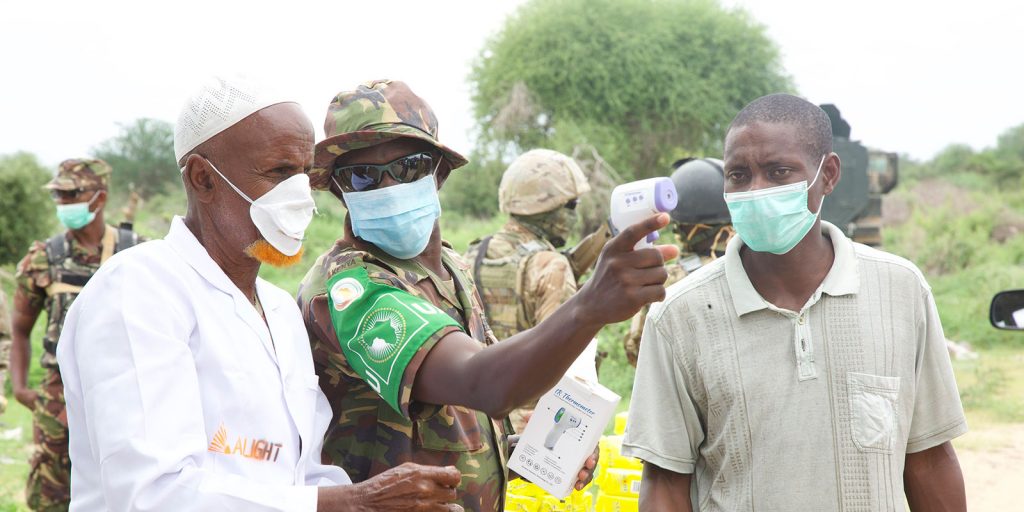

The African Union (AU) mission in Somalia (AMISOM) has been deployed in Somalia since 2007 and has significantly improved the security situation in Somalia. The main insurgency group, Al-Shabaab, is still present in most areas of Somalia. The postponed elections have created increased political tension and confrontations between the security forces and opposition supporters. The deterioration in the political situation constitutes a direct threat to the gains made since 2007. This takes place against the backdrop of COVID-19, which in recent weeks, has caused a rise in positive cases thereby exacerbating an increasingly difficult humanitarian crisis.
The State of Somalia: Electoral Impasse and Growing Insecurity
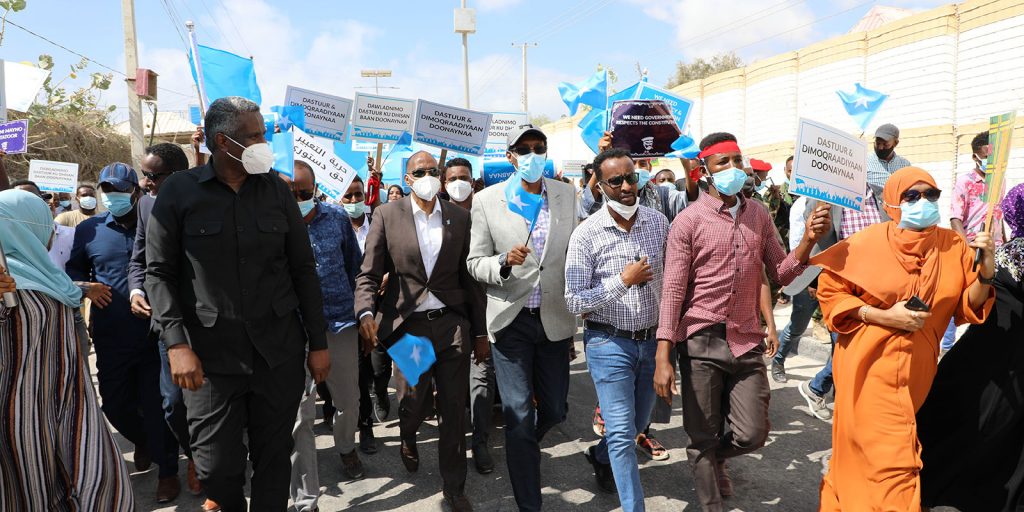

At the time of writing, the term of Somalia’s bicameral parliament and the presidency have both expired. Between July and September 2020, four conferences were held and attended by leaders of the Federal Government of Somalia (FGS) and the Federal Member States (FMS). Led by Somalia’s President Mohamed Abdullahi ‘Farmaajo’, three out of the four conferences ended without an agreement that had the full consensus of all parties. Since the establishment of a Federal Somalia in 2004, there has been a contentious relationship between the centre (FGS) and periphery (FMS), stemming from the lack of consensus on the nature and the scope of Somalia’s federation. This tense relationship has contributed to a fragmented political environment that has hindered a common agenda on national priorities. With no meaningful amelioration during President Farmaajo’s four-year term, this state of affairs has negatively impacted Somalia as it enters national elections in February 2021.
The Impact of Climate Change on Peace and Security in Somalia: Implications for AMISOM
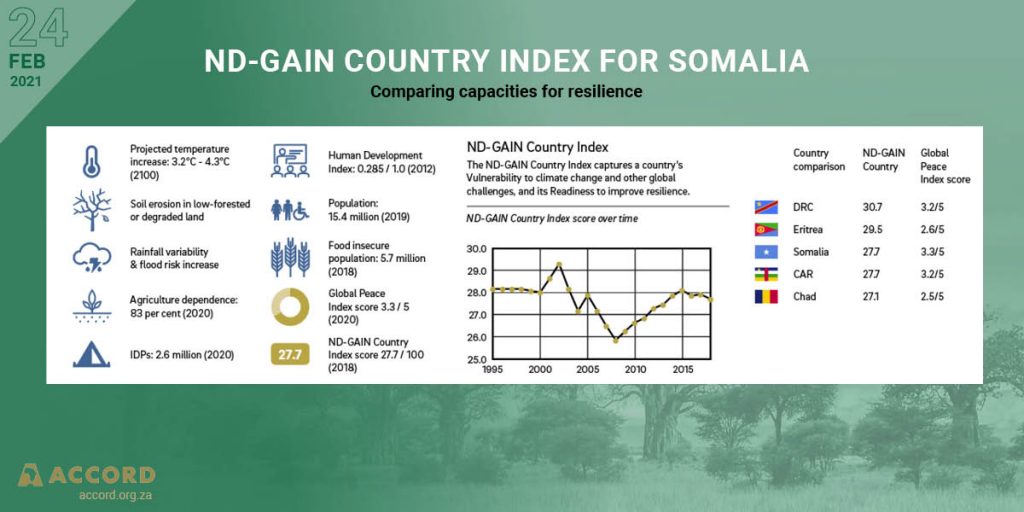
The February 2021 mandate renewal for the African Union Mission in Somalia (AMISOM) is an opportunity to review what we know about climate change and security in Somalia, and to consider what governments and multilateral organisations can do to improve the way they manage climate related security risks. Research finds no direct causal relationship between climate and conflict but has identified multiple pathways through which climate-related change interacts with political, social, and environmental stresses to compound existing vulnerabilities and tensions. These factors combined can undermine development gains, impact the dynamics of ongoing violence and disrupt fragile peace processes. Additional pressures, such as COVID-19, compound the risk and makes a country like Somalia even more vulnerable to shocks and setbacks, as the recent political crisis shows.
From National Interest to Global Responsibility: Vaccine Nationalism and the World Trade Organisation (WTO)
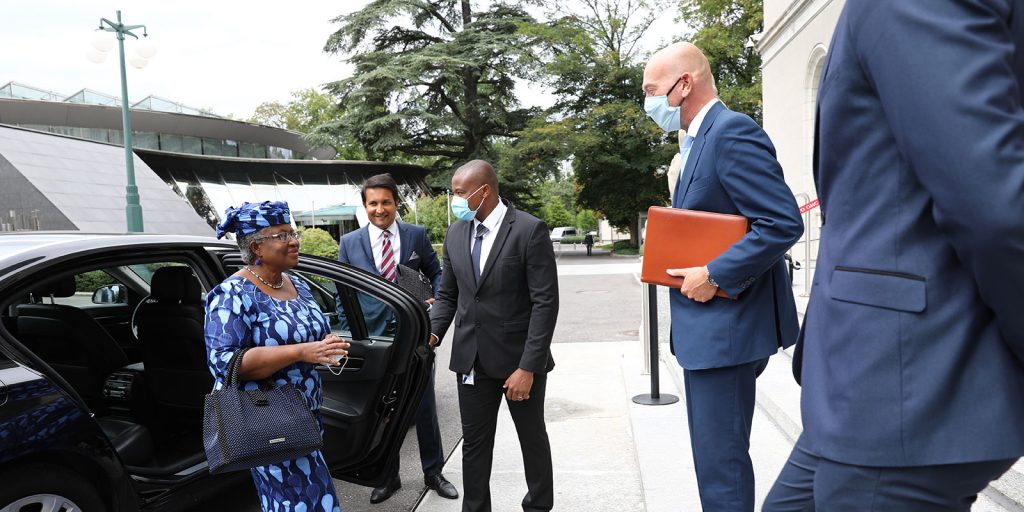

The 15th of February 2021 will go down in history as the day on which a woman, and an African, was elected for the first time to the important post of Director-General of the WTO. It is a proud day for women all around the world and a proud day for all of us in Africa. However, Dr. Ngozi Okonjo-Iweala, had to wait several months for a change in the administration of the United States before there could be consensus on her appointment, despite her having the support of the overwhelming majority of the members of the WTO. This very fact underscores the vital importance of this job at this particular juncture in our world.
The 34th summit of the African Union: COVID-19, New Leadership and Africa’s Arts
The 34th ordinary session of the African Union (AU) Assembly took place without the usual fanfare. Held away from the gaze of the public via an online platform courtesy of the COVID-19 pandemic, the AU summit set by design a very limited agenda. Apart from the transition of the leadership of the AU Assembly from South Africa’s President Cyril Ramaphosa to Felix Tshisekedi of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), and an update on the institutional reform of the AU, the summit focused, in the main, on the election of the new leadership of the AU Commission and Africa’s response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Making the First Elections Count: Implementing the African Union Institutional Reform Process
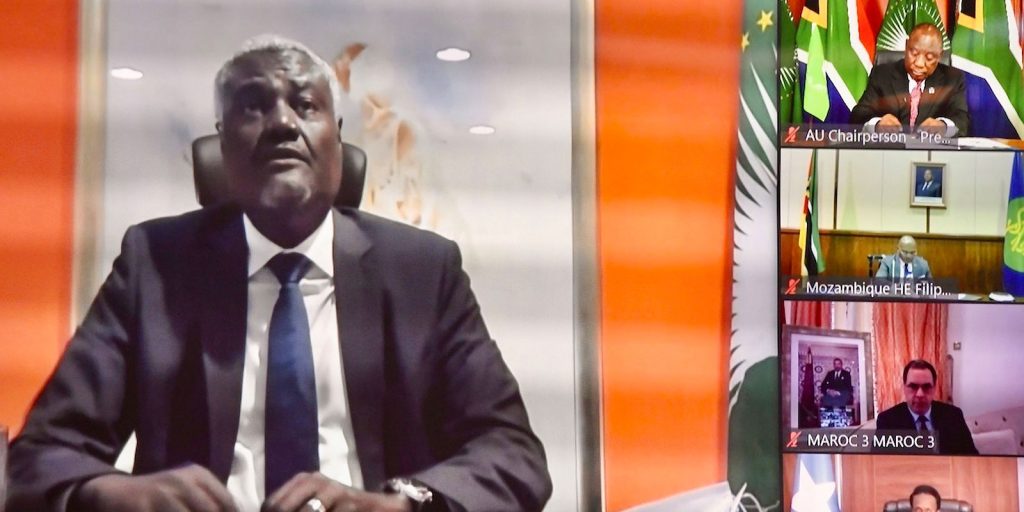

The 2021 elections of the top leadership team of the African Union Commission (AUC) were historic because they were the first following the adoption of the institutional reform process of the Union. It was therefore the litmus test for the proposed reforms adopted by the Union in 2018 particularly concerning the election of the senior leadership of the Commission. Of particular importance is that according to the reforms the chairperson, deputy chairperson and six commissioners have to be, on a rotational basis, representative of the five regions of Africa and the team has to be gender balanced.
