COVID-19, Resilience and South-South Cooperation

The COVID-19 crisis has wreaked havoc across the world and changed our understanding of the relationship between health and governance in many ways. With the virus having affected over 150 million people all over the world in a period of 12 months, it has become the biggest health crisis the world has faced in many decades.
An African Peace Engineering Corps can help the continent respond to COVID-19 and other such emergencies
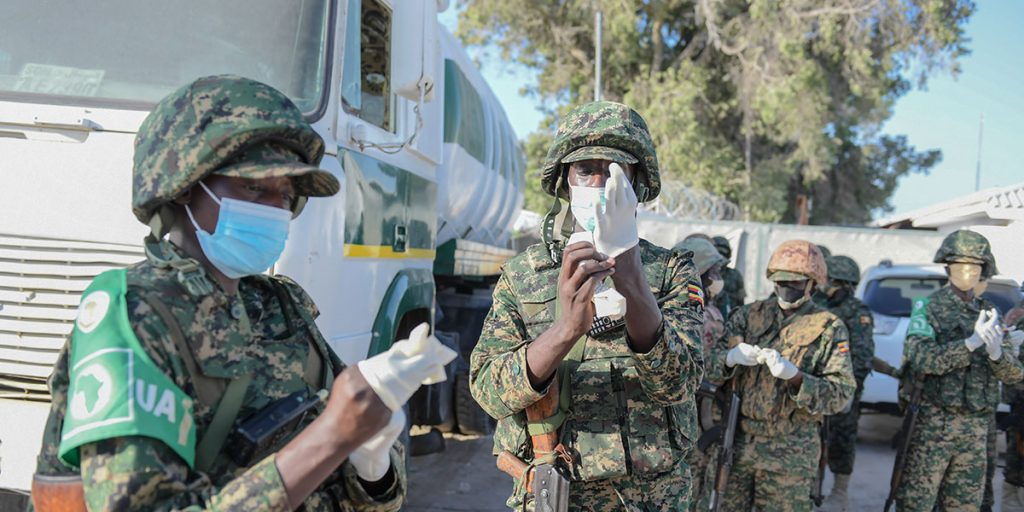

When in 2013, the devastating Ebola Virus Disease broke out in Guinea, it did not only spread to Sierra Leone and Liberia; it also threatened the world. By the time the outbreak ended in 2016, Sierra Leone, Guinea and Liberia, had lost over 11,000 people and $2.8 billion in GDP losses, according to the World Bank.
COVID-19 Conflict & Resilience Monitor – 5 May 2021

During the COVID-19 crisis ACCORD’s analysis is focused on the impact of the pandemic on conflict and resilience in Africa.
Tanzania’s COVID-19 Strategy: Local and Regional Implications
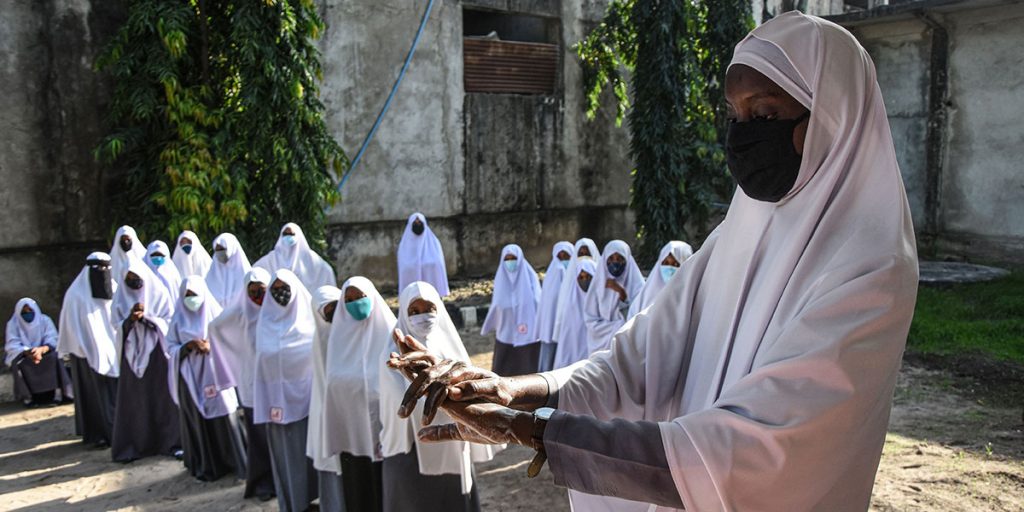

Tanzania’s COVID-19 strategy has been a mixed-bag of admission, denialism, pragmatism and tiptoeing. At the centre of this approach has been the country’s late President John Magufuli whose actions and statements defined the country’s COVID-19 policy.
The role of the religious community in peacekeeping: the page that was lost in Cabo Delgado

Peace is undoubtedly the basis for the development of any society, especially for developing countries. In Africa, peace may be accepted as the absence of armed conflicts or the silence of weapons – even though poverty, the result of injustice and social inequalities, exacerbated by the unequal distribution of wealth, as well as corruption, unemployment and natural disasters, among other evils, are prevalent throughout the continent – and this much desired laying down of arms and absence of armed conflicts by a considerable number of African countries is an essential condition for combating poverty, restoring justice, socioeconomic and political stability, and sustainable development, including at regional and continental levels.
Lessons for Cabo Delgado from the African experience in Somalia
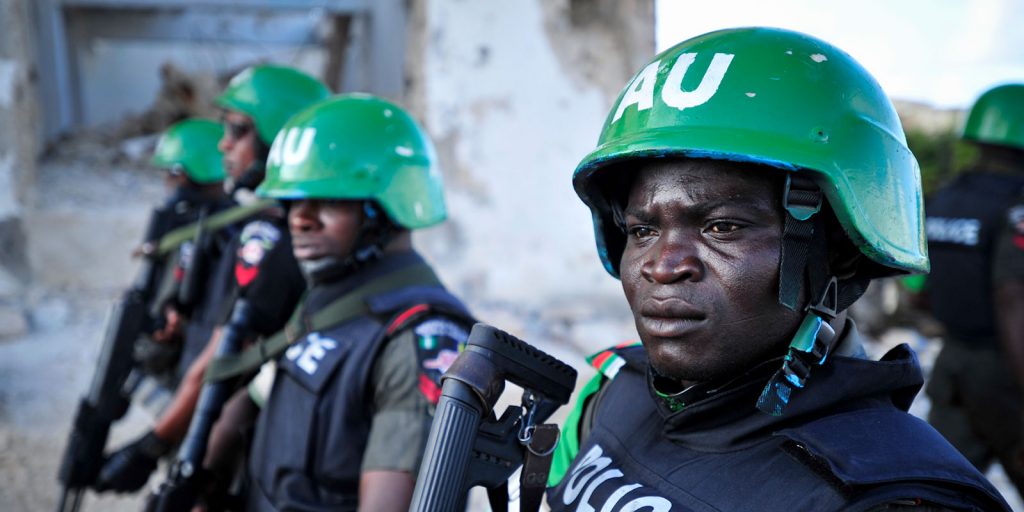

What can we learn from the African Mission in Somalia (AMISOM) for Cabo Delgado? One key lesson from the Somalia experience is that a security operation like AMISOM can create the opportunity for stabilisation, but for that opportunity to be turned into reality one needs a significant focus on political engagement, governance, rule of law, basic services and socio-economic development.
An overview of the conflict in Cabo Delgado: narratives, causes and strategies on the way forward

On 5 October 2017, unknown armed men attacked the town of Mocimboa da Praia, in the far North of the Mozambican province of Cabo Delgado. The attack primarily targeted government institutions, with a focus on police stations. The attack was later determined to have been carried out by members of the local communities, primarily young Muslim men. The government’s security forces acted quickly to stop the attacks and keep the situation under control. As a result, some of the attackers were either killed or arrested. This appears to have infuriated them, as they simply went underground and metamorphosed into guerrilla units capable of confronting government security forces after three years.
The Cabo Delgado conundrum amidst the COVID-19 crisis: fostering resilience through inclusive development, peacebuilding, and prevention of violent extremism
On 22 March 2020, the first case of COVID-19 was announced in Mozambique, followed by the government’s declaration of its first state of emergency on 1 April 2020. In the northern region of Cabo Delgado and neighbouring provinces, the spread of the virus is of additional relevance as, at the time of writing, more than 670,000 people have been displaced due to violent extremist attacks.
Lessons learned from the G5 Sahel Force for Mozambique, SADC and the AU

The Group of Five for the Sahel, commonly known as the G5 SAHEL was created in 2014 by the governments of Burkina Faso, Chad, Mali, Mauritania and Niger as a platform to collectively address the development and security challenges confronting them. When carefully analysed, one can see some similarities between Cabo Delgado’s growing challenges with violent extremism and the case of the Sahel.
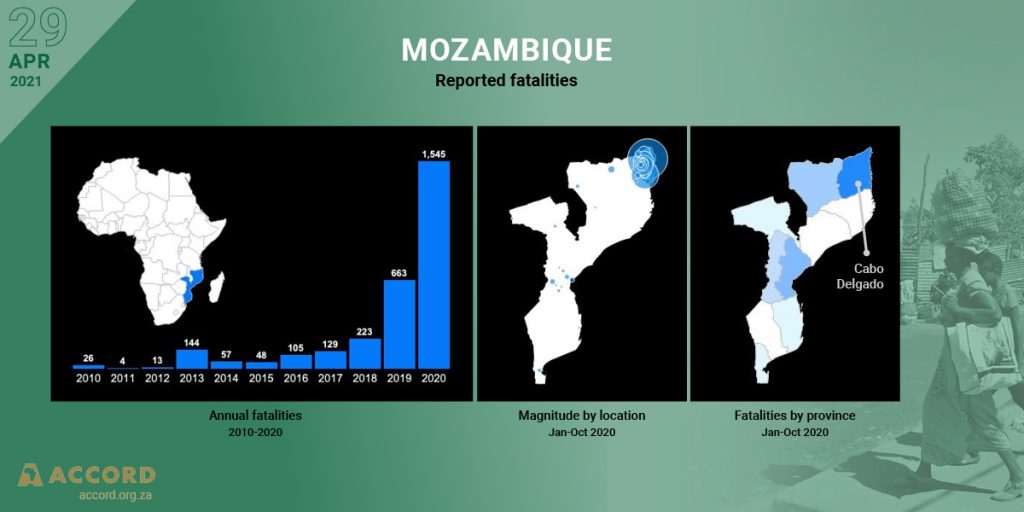
COVID-19 Conflict & Resilience Monitor – 29 April 2021

During the COVID-19 crisis ACCORD’s analysis is focused on the impact of the pandemic on conflict and resilience in Africa.
