The agency of southern African youth during the COVID-19 pandemic

In a year dedicated to Silencing the Guns (STG) in Africa, the world has been plunged into a global pandemic that risks reversing the gains made on the peace and security front on the continent, either by creating new forms of conflicts or exacerbating already-existing ones. While the African Union (AU) and regional economic communities (RECs) – such as the Southern Africa Development Community (SADC) – concurrently seek to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic while attending to rising conflicts, this piece spotlights the agency of youth in the region and why it matters in emerging conflicts.
The impact of COVID-19 in the SADC region: building resilience for future pandemics

The COVID-19 pandemic has brought multiple challenges to the Southern African Development Community (SADC) as a region and to its member states. Some of these challenges include the unavailability of medicines and health equipment, food insecurity, gender-based violence and a negative impact on the economies of member states. Whilst the pandemic has exacerbated existing challenges, the region has continued to defy some of the early forecasting that Africa would be hardest hit by COVID-19, following what happened in developed countries with better-resourced health systems. The region has thus shown a greater degree of resilience, demonstrating that lessons are not only learnt from developed countries.
COVID-19 and African indigenous peoples: Cameroon’s Pygmies, Mbororo and Kirdii
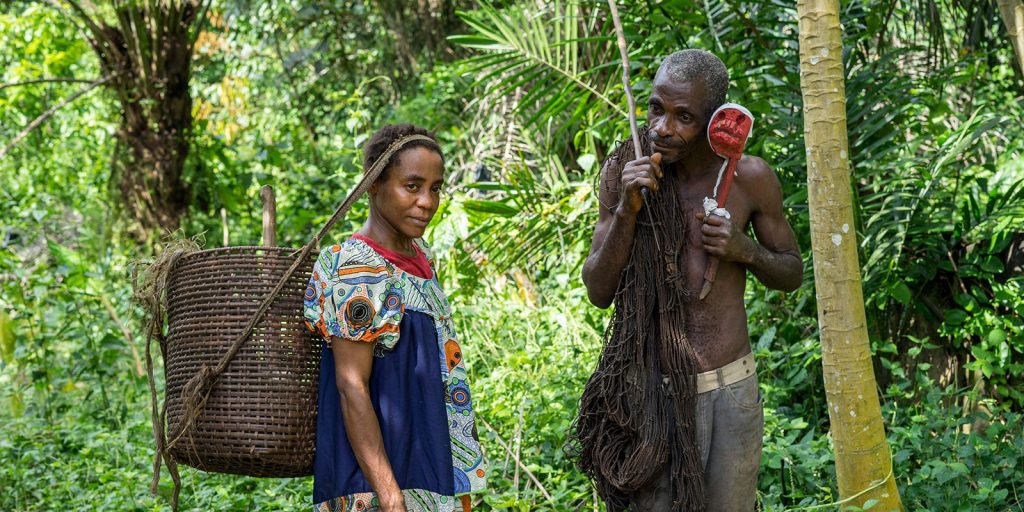

Absent from the dominant narrative about the societal impact of COVID-19 has been the plight of indigenous peoples, who tend to disproportionately experience higher rates of infection, particularly women when confronted with health crises emerging from modern pandemics. This is linked to cultural factors, as well as weakened access to healthcare and linguistic differences that contribute to higher rates of infection.
Despite COVID-19, Civil Society Remains as the Vanguard of the Women, Peace and Security Agenda in Africa
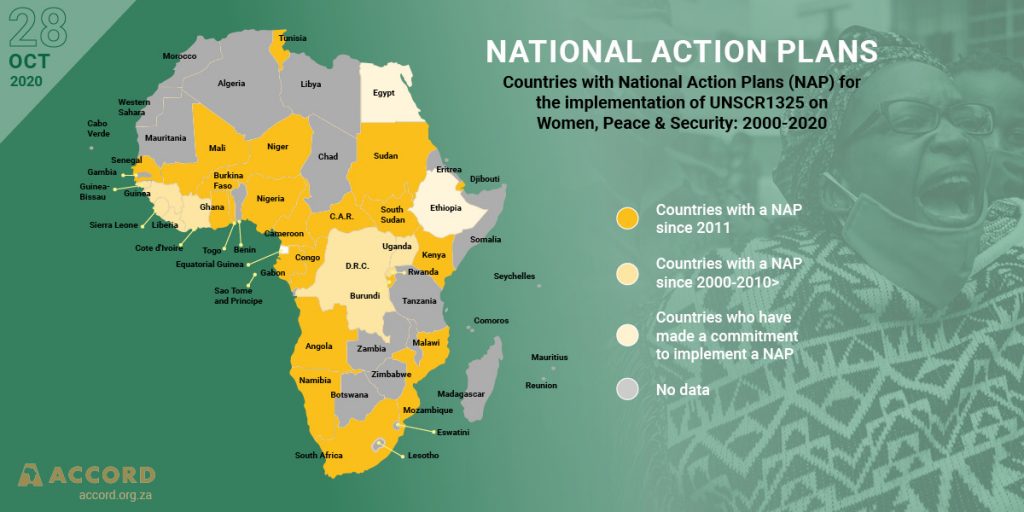
This year we celebrate two defining milestones in the Women, Peace and Security Agenda, namely the 25th anniversary of the Beijing Declaration and Platform for Action and the 20th anniversary of United Nations Security Council Resolution (UNSCR) 1325 of 2000. 2020 will also be remembered for the COVID-19 pandemic. How the pandemic will redefine the role of women in the peace and security context is still not clear. However, it seems COVID-19 has not been able to disrupt the fortitude and commitment of civil society in Africa. It was civil society that realised UNSCR 1325 in 2000 and it will be civil society that safeguard and implement UNSCR 1325 in 2020 and beyond, through their activism, advocacy, capacity building and conflict resolution practice.
Twenty Years of UNSC Resolution 1325 call for a Frank Forward Look

Since the United Nations (UN) adopted UN Security Council Resolution (UNSCR) 1325 on Women, Peace and Security (WPS) in 2000 there have been significant shifts in discourse and practice on gender, peace and security. Twenty years later, conscious of the original limitations that shaped UNSCR 1325 in the first place, we must account for these shifts whilst striving to do much more than simply sustain the agenda.
Reinforcing The Role of Women in Mediation, amidst COVID-19
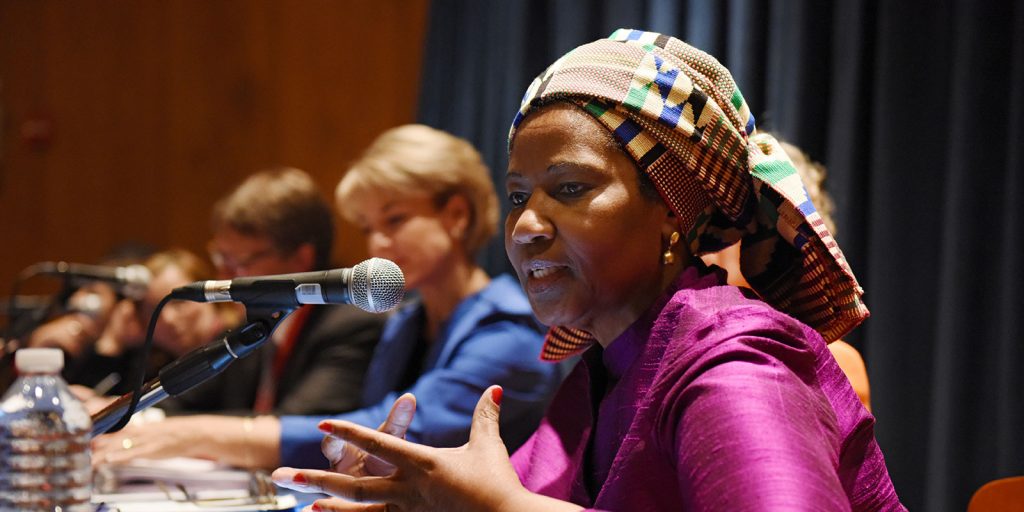

On 31 October 2000, the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) passed the landmark resolution 1325. The resolution represents a victory for women as a global recognition of their legitimate right to protection and participation in peace processes at all levels, and an acknowledgement of the world’s responsibility to prevent and address gender based violence.
COVID-19 and the Anniversary of UNSC Resolution 1325 on Women, Peace and Security
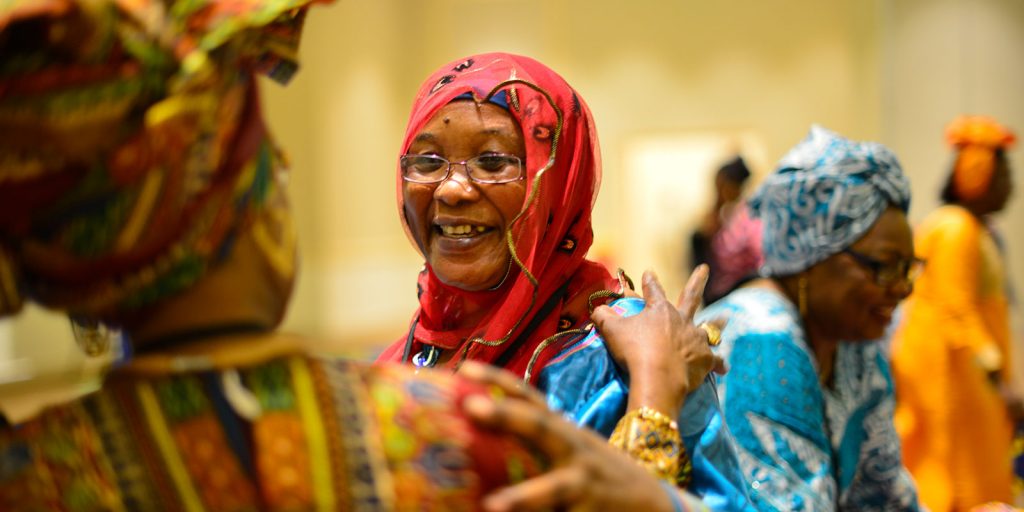

Women’s meaningful participation in peace processes is a cornerstone of the United Nations Security Council Resolution 1325 on the Women, Peace and Security (WPS) agenda. As we commemorate the 20th anniversary of this landmark Resolution for WPS, we the Co-Chairs of the Network of African Women in Conflict Prevention and Mediation (FemWise-Africa) want to take the opportunity to highlight the work of Africa’s conflict prevention and mediation networks and their determination to ensure that the next twenty years for WPS will not be the same.
The New Idea of Africa in the Context of COVID-19

COVID-19 has created a global uncertainty: everyone everywhere is thinking about the possibilities of premature death. This uncertainty is upon all of us, but the African continent in particular, and the Global South in general, have been facing this uncertainty and this possibility of premature death for a very long time. Because of that, we will need to shift the geography of knowledge and even the biography of knowledge and begin to think about what is it that the Global South can offer us in dealing with this pandemic. What can we gain from indigenous African knowledges and epistemologies of the Global South? This argument arises because the Global South in general, and the African continent in particular, have some of the richest histories and experiences of dealing with epidemics and pandemics.
Reflections on the Impact of COVID-19 on Africa’s Higher Education and Research Sector
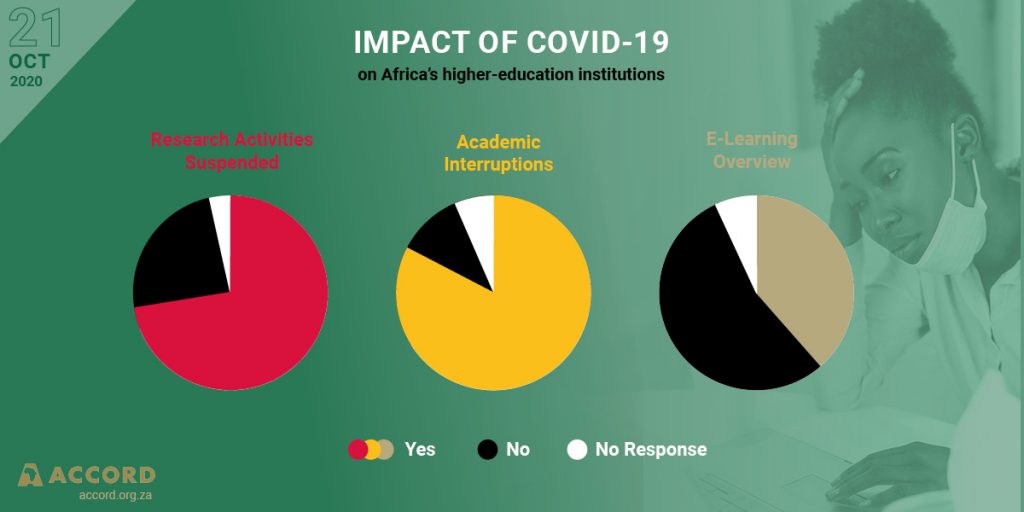
Academic and research institutions find themselves tasked with learning how to adapt in real-time amid the COVID-19 pandemic that is significantly disrupting the global higher education sector. Most of the focus so far has been on western countries, leaving major gaps in our understanding of how Africa’s own centres of knowledge production are faring in this crisis. We know that the state of research and higher education on the continent has long been a cause for concern even before the COVID-19 crisis, and early indications show that the virus is exacerbating these vulnerabilities.
The Impact of COVID-19 on Universities in Africa

The COVID-19 pandemic has brought unprecedented disruption and uncertainty to universities in Africa. It forced the higher education sector in Africa to make changes that were long overdue by magnifying existing challenges to students’ ability to engage with their learning. COVID-19 has forced universities to recognize that the future is now. For years, many universities and governments have been talking about the need for online education or blended learning models in which at least part of a student’s education is captured online through a learning management system. However, many schools have been slow to respond to this call. COVID-19 has forced universities to either adapt quickly to an online delivery system or to stall and risk obsolescence.
