Actions taken by the Economic Community of Central African States in response to COVID-19
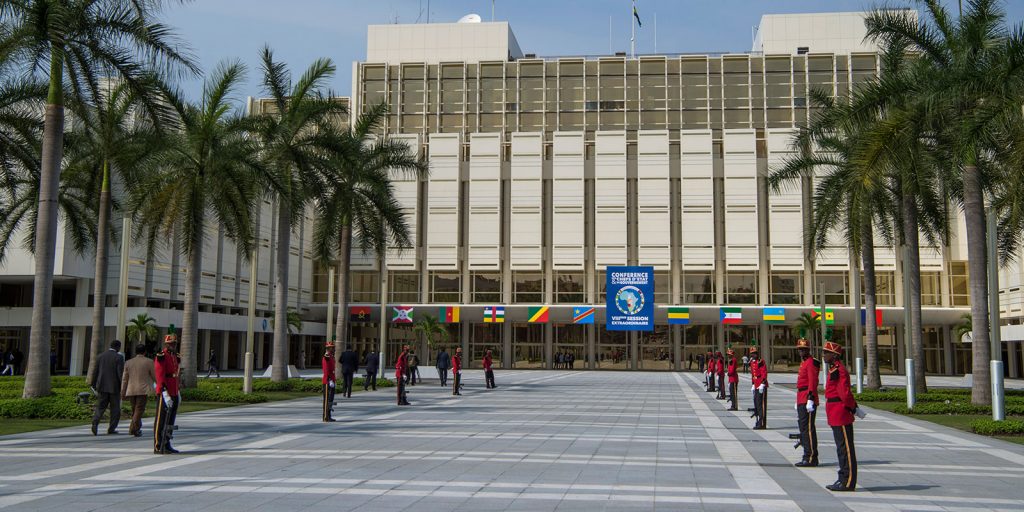

Like all other parts of the world, the Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS) has been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic since 6 March 2020 and all eleven member countries had registered their first cases by 6 April 2020. In addition to a number of steps taken by ECCAS, plans are also moving forward to establish a sub-regional body for the coordination of health issues in ECCAS.
COVID-19 Conflict & Resilience Monitor – 1 April 2021

During the COVID-19 crisis ACCORD’s analysis will be focused on the impact of the pandemic on conflict and resilience in Africa.
Mediating in a Time of COVID-19

Mediation in situations of civil conflict are never easy. It requires travel, both air and on the ground, sometimes to far off areas where the terrain may not be easy to traverse. It also requires confidential face-to-face discussions and, when momentum towards an agreement is detected, then time becomes a valuable commodity, and shuttling between parties to narrow differences, and edge towards a compromise, becomes vital.
The Case for a more Prosperous and Stable Country: What is at Stake in the DRC?

It will take more than just the political will of international and national actors to pave a smooth path for long-term stability in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). Based on its security, social, and political dynamics, the DRC needs a total rebuilding of its institutions.
Sudan: Displacement in the context of COVID-19
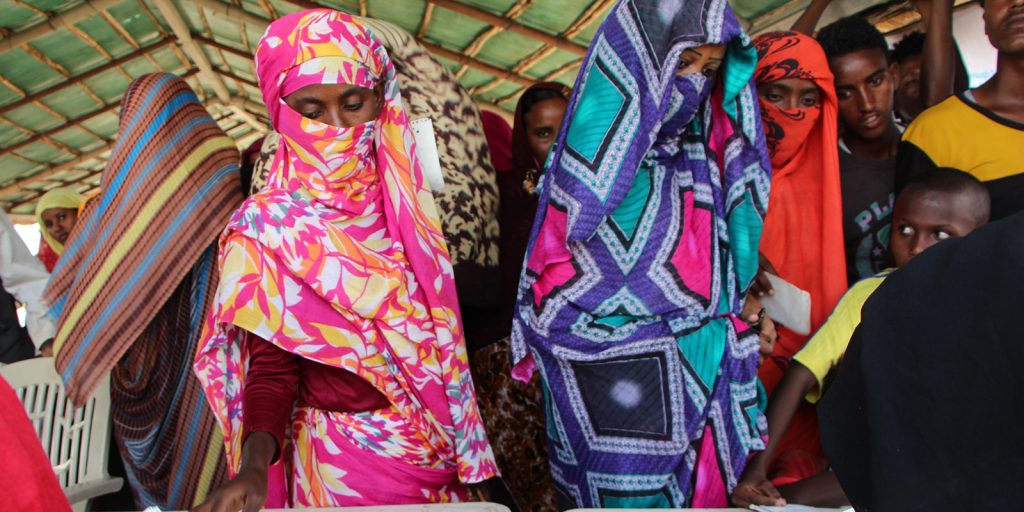

Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic one year ago, the Horn of Africa region has experienced a proliferation of conflict and inter-state tensions. This has served to exacerbate the already dire displacement and refugee situation in the region, with thousands fleeing their homes in search of security, which is not often easily found. These difficulties are being aggravated by the COVID-19 pandemic and its associated challenges.
South Sudan’s battle for Democracy
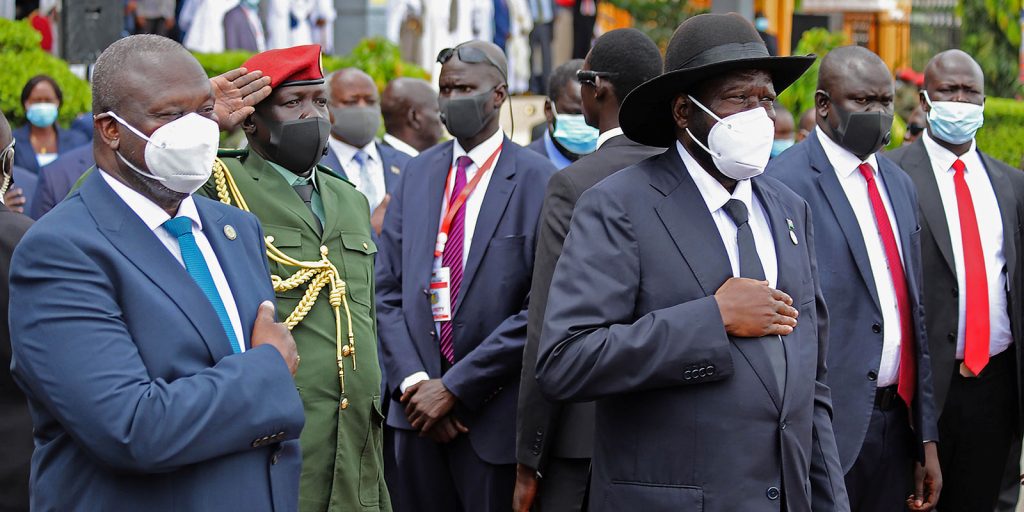

South Sudan’s peace process is still largely up for negotiation. A new South Sudan must emerge through a civilian technocratic government. This will require transforming the way security forces control the state. It also means being serious about addressing the root causes of conflict, implementing a transitional parliament, drafting a new constitution, deciding what type of federalism best suits the country and strengthening the electoral commission.
COVID-19 Conflict & Resilience Monitor – 24 March 2021

During the COVID-19 crisis ACCORD’s analysis will be focused on the impact of the pandemic on conflict and resilience in Africa.
Climate, Peace and Security: The case of South Sudan
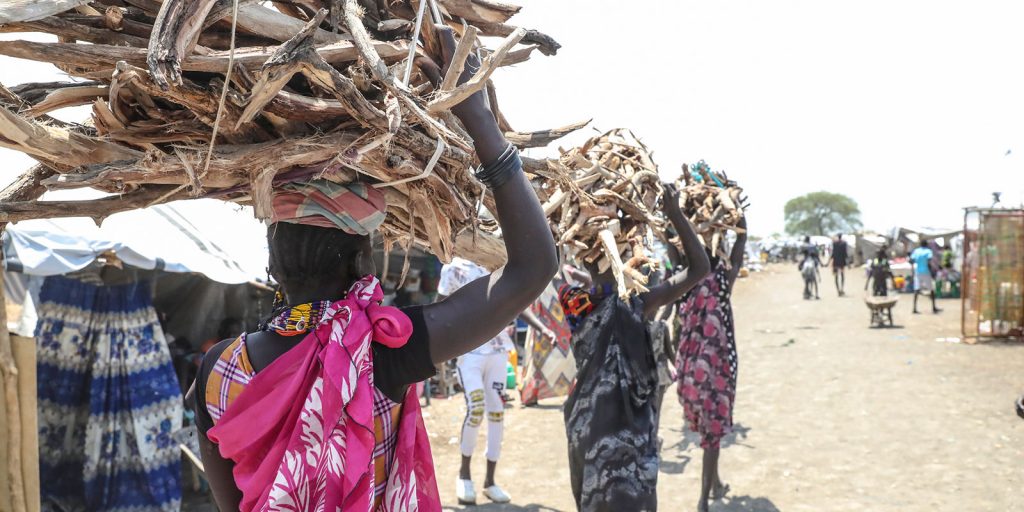

South Sudan is the world’s youngest nation and one of the least populated countries in Africa, but also one of the most vulnerable to climate change. The consequences of climate change can worsen South Sudan’s humanitarian crises and fragile security environment, marked by widespread communal conflict and a civil war since 2013. With a population estimated at 11 million, more than 1.6 million people have been internally displaced due to prolonged conflict.
A critical year ahead for the UN Mission in South Sudan
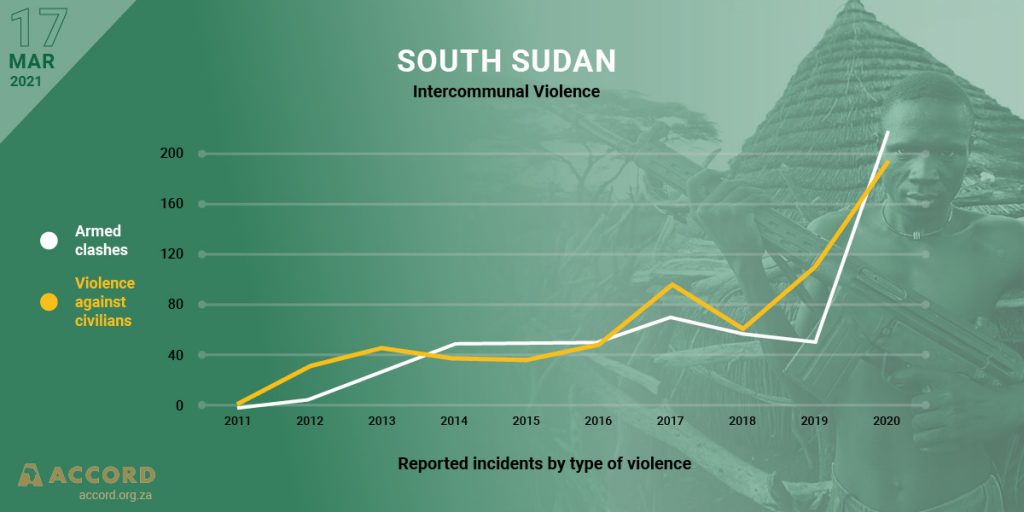
The peace process in South Sudan is still highly vulnerable to relapse. Although the Revitalized Peace Agreement has brought large-scale fighting to an end, inter-communal conflict has flared up and will most likely be a major cause of instability and displacement in the year ahead. The implementation of the peace agreement has been slow and uneven with the parties mainly focused on elite power-sharing arrangements. In the meantime, the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has contributed to delaying the full implementation of the peace agreement and it has also disrupted the work of the United Nations. The UN Mission in South Sudan (UNMISS) has implemented enhanced mitigation and prevention measures after a recent significant increase in COVID-19 cases in South Sudan, which has been mirrored by an increase in cases among UN personnel.
Continuity and Change in European Union-Africa Relations on Peace and Security

The European Union (EU) and the African Union (AU) maintain a long-standing partnership on peace and security which can be qualified as constructive. It is largely based on joint interests and objectives and is less contentious compared to other more challenging topics, such as migration and trade. The EU’s new seven-year budget for 2021 – 2027 introduces new ways of working which impact on how the EU will engage on peace and security in Africa. Most notable in this regard is the establishment of the European Peace Facility (EPF) which can potentially undermine the AU’s role in leading and coordinating peace and security measures on the continent. Moreover, these new developments take place against the backdrop of an overall troubled EU-AU relationship which suffers not only from the divergences in interests in key areas such as migration, trade and climate but also from the consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic, and global geopolitics.
